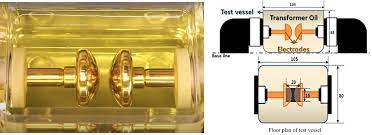
The dielectric strength of transformer oil is also known as the breakdown voltage (BDV) of transformer oil. Breakdown voltage is measured by observing at what voltage, sparking strands between two electrodes immersed in the oil, separated by a specific gap. A low value of BDV indicates presence of moisture content and conducting substances in the oil.
For measuring BDV of transformer oil, portable BDV measuring kit is generally available at site. In this kit, oil is kept in a pot in which one pair of electrodes are fixed with a gap of 2.5 mm (in some kit it 4mm) between them. Now slowly rising voltage is applied between the electrodes. The rate of rising voltage is controlled at 2 KV/s and observe the voltage at which sparking starts between the electrodes. That means at which voltage dielectric strength of transformer oil between the electrodes has been broken down.
This measurement is taken 3 to 6 times in the same sample of oil, and we take the average value of these readings. BDV is an important and popular test of transformer oil, as it is the primary indicator of the health of oil and it can be easily carried out at the site.
Dry and clean oil gives BDV results, better than the oil with moisture content and other conducting impurities. Minimum breakdown voltage of transformer oil or dielectric strength of transformer oil at which this oil can safely be used in transformer, is considered as 30 KV.
